Drones
What are Drones?
A drone, also known as an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), is an aircraft that operates without a human pilot onboard. Drones come in various shapes and sizes, from small handheld devices to large, more sophisticated aircraft. They can be controlled autonomously by computers or remotely by a human operator on the ground. Equipped with multiple rotors or propellers, drones can hover, take off, land, and navigate within different environments. Their applications range from capturing breathtaking aerial photographs and videos to assisting in search and rescue missions.
Drones in the Aerospace Industry
Drones have dramatically transformed the landscape of aerospace engineering and are set to play an increasingly vital role in the future. Beyond their original military applications, drones now find use in a wide range of commercial, scientific, and even recreational contexts. Here are some key points about drones in the aerospace industry:
Commercial Applications
- Farming & Agriculture: Drones assist farmers by monitoring soil and crop health, applying water and fertilizers, tracking weather, and collecting data for yield estimations.
- Business: UAVs are changing the status quo across various industries. Examples include photography, videography, shipping/delivery services, aerial surveying, and site inspections.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry explores drones for inspecting commercial aircraft. These drones can significantly reduce inspection time, improve accuracy, and enhance safety by identifying faults and sending service work orders promptly.
Challenges and Regulations: Drones have operated under temporary regulations due to their rapid adoption. Policy regulators are catching up with the technology’s wide array of applications. Balancing innovation with safety and privacy remains a challenge, but ongoing advancements promise exciting developments in the aerospace sector.
Space-Compatible Drones
To operate in space, drones must undergo significant modifications. These adjustments account for the unique conditions, including low atmospheric pressure and weak gravity.
- Space Exploration Drones: While not a traditional drone, NASA’s X-37B is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed for space missions. It demonstrates the potential for combining drone technology with space exploration.
- Recent Milestone: NASA’s Ingenuity, a small helicopter-like drone, successfully flew on Mars. It marked the first time drone technology was tested on another world.
In summary, while everyday drones won’t explore deep space, specialized UAVs and spacecraft continue to push the boundaries of aerial exploration beyond Earth.
Evolution of Drones
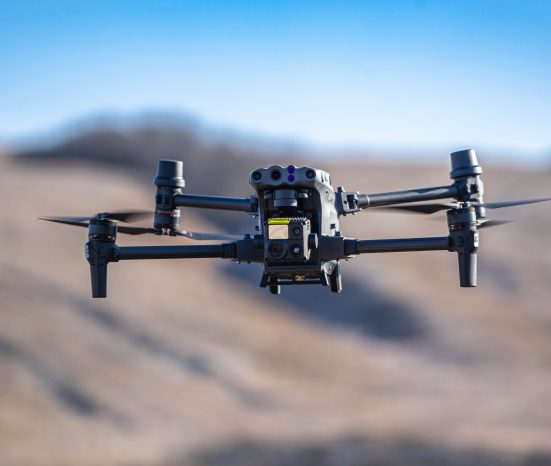

The evolution of drones began with their military applications in the early 20th century, primarily for reconnaissance and surveillance. Over the decades, advancements in technology, including miniaturization of sensors and improvements in battery life, enabled the development of smaller, more agile drones suitable for commercial and consumer use. By the 2010s, drones had expanded into various industries such as agriculture, construction, and cinematography, revolutionizing operations with their capabilities in aerial imaging, mapping, and remote sensing. Today, ongoing research focuses on enhancing drone autonomy, safety features, and regulatory frameworks to support their integration into mainstream airspace.
Aerospace & Drones in Future
In the future, drones are expected to play a pivotal role in the aerospace industry by augmenting traditional aviation operations and enabling innovative applications. They will likely enhance surveillance and monitoring capabilities, providing real-time data for air traffic management and disaster response. Additionally, drones could facilitate last-mile delivery services for parts and supplies in aerospace manufacturing, reducing logistical challenges and improving efficiency. Continued advancements in drone technology, including increased autonomy and payload capacity, will further expand their utility across aerial inspections, environmental monitoring, and even passenger transport in urban air mobility initiatives.

Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions and answers pertaining to drones, especially in regards to aviation.
How are drones used in aviation?
Drones are used in aviation for various applications including aerial photography and videography, infrastructure inspection, surveying, environmental monitoring, and even passenger transport in emerging urban air mobility projects.
What are the regulations for flying drones near airports and in controlled airspace?
Regulations typically require drone operators to obtain permissions or licenses, adhere to altitude and distance restrictions from airports, and comply with airspace regulations set by aviation authorities to ensure safety and prevent interference with manned aircraft.
What safety measures are in place to prevent drone collisions with manned aircraft?
Safety measures include geo-fencing technology that limits drone flight near airports and critical airspace, mandatory registration of drones with aviation authorities, use of detect-and-avoid systems on larger drones, and pilot training and certification requirements.
How does drone technology contribute to aviation safety and efficiency?
Drones contribute to aviation safety by performing inspections of infrastructure like runways and aircraft, monitoring wildlife activity near airports to prevent bird strikes, and providing real-time data for weather monitoring and emergency response operations.
What are the challenges facing the integration of drones into mainstream aviation operations?
Challenges include ensuring robust communication and navigation systems for drone traffic management, addressing public concerns about privacy and airspace congestion, developing standardized protocols for drone operations, and adapting existing air traffic control systems to accommodate unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Video Explanation
The video below will provide more information as to how this technology works
Example Industry User

Airborne Platforms UK specializes in the deployment of drones for various applications, including surveillance, environmental monitoring, and marketing. They provide training to obtain drone licenses and their expertise enables them to offer cutting-edge capabilities for civilian use. This relationship underscores Airborne Platforms UK’s commitment to harnessing drone technology to address complex challenges and deliver superior aerial solutions.
Further Resources
Below are some external links to further information on this technology.