Robotics
What is Robotics?
Robotics is an interdisciplinary field that combines science, engineering, and technology to create machines called robots. These robots can replicate or substitute for human actions. Here are some key points about robotics:
Definition: Robotics involves designing, constructing, and operating machines (robots) that can perform tasks traditionally done by humans. These tasks can range from simple, repetitive actions to more complex activities.
Types of Robots
- Industrial Robots: Used in manufacturing and assembly lines to perform tasks with precision and efficiency.
- Service Robots: Assist humans in various settings, such as cleaning robots, medical robots, and delivery drones.
- Exploration Robots: Used for space exploration (like the Mars rovers) or underwater exploration.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars and drones fall into this category.
Components of a Robot
- Mechanical Construction: The physical structure of a robot, including its moving parts.
- Electrical Components: Power sources (like batteries) and control systems.
- Software Programming: Robots need code to know how to carry out specific tasks.
Levels of Autonomy
- Human-Controlled: Bots that follow instructions from a human operator.
- Semi-Autonomous: Can perform tasks with some autonomy but still require human oversight.
- Fully Autonomous: Operate independently without external influence.
Robots in Aerospace
Aerospace robots are industrial robots designed to assist people and manufacturing processes in the aerospace industry. They serve various purposes, from precision manufacturing to research and development. Here are some key points:
Types of Aerospace Robots
- Robotic Arms: Used in production assembly lines to ensure precise measurements and specifications.
- Autonomous Drones: Used for aerial surveys, inspections, and data collection.
History
- Early Beginnings (1960s): Automated machines for repetitive tasks in aircraft manufacturing.
- Space Exploration (1970s-1980s): Introduction of robotic systems like the Canadarm.
- Modern Applications: Aerospace robots are now integral to manufacturing, maintenance, and safety in the industry.
Benefits
- Efficiency: Robots streamline processes and enhance productivity.
- Quality Assurance: Precise measurements meet stringent standards.
- Innovation: Opens new avenues for advancement.
Robotics Engineering
Aerospace engineering involves designing, creating, overseeing, and testing aircraft, spacecraft, navigation systems, satellites, and missiles. On the other hand, robotics engineering focuses on designing, building, and maintaining robotic systems to facilitate or replace human activities. While these fields are distinct, they intersect when it comes to aerospace robots. Here’s how robotics plays a role in aerospace:
Welding
- Automated welding robots enhance safety and speed up aircraft manufacturing.
- They handle materials like nickel-alloy or titanium with precision.
- Result: Safer aircraft, improved structural integrity, and increased productivity.
Sealing, Painting, and Coating
- Repetitive processes like sealing, painting, and coating are time-consuming.
- Robotics frees up human workers by automating these tasks.
- Consistent quality and efficiency are achieved.
Drilling and Fastening
- Robotics significantly impact the drilling and fastening process.
- Assembly line employees find this job tedious and lengthy.
- Robots streamline these critical steps in aerospace manufacturing.
In summary, aerospace robotics is crucial for efficiency, safety, and quality in the industry.
Evolution of Robotics
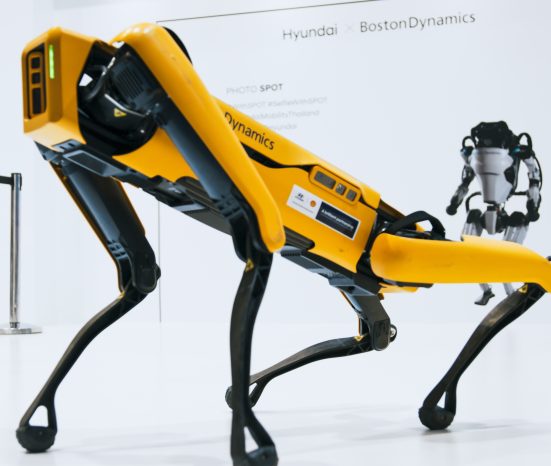

The evolution of robotics has seen remarkable advancements from simple mechanical devices to sophisticated autonomous systems. Early robots were primarily used in industrial settings for repetitive tasks, but advancements in computing power, sensors, and artificial intelligence have expanded their capabilities. Modern robots are now capable of complex interactions, ranging from medical surgeries and space exploration to everyday household tasks. As technology continues to progress, robotics is poised to play an increasingly integral role in various sectors, enhancing efficiency, precision, and the ability to perform tasks in hazardous environments.
Aerospace & Robotics in Future
The future of aerospace will see robotics playing a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, safety, and exploration capabilities. Robots are expected to assist in spacecraft assembly and maintenance tasks in space, reducing human risk and extending mission durations. On Earth, robotic systems will revolutionize aircraft manufacturing processes, increasing precision and productivity in complex assembly tasks. As technology advances, collaborative efforts between robotics engineers and aerospace experts will unlock new possibilities for space exploration and aircraft innovation, shaping the future of aviation and space travel.

Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions and answers pertaining to robotics, especially in regards to aviation.
How are robotics used in aviation manufacturing?
Robotics are utilized in aviation manufacturing for tasks such as precision assembly of aircraft components, welding, painting, and quality inspection, improving efficiency and consistency in production processes.
What role can robotics play in aircraft maintenance?
Robotics can assist in aircraft maintenance by performing inspections, repairs, and routine tasks in challenging or hazardous environments, reducing downtime and enhancing safety for maintenance crews.
How might robotics improve airport operations?
Robotics can streamline airport operations by automating baggage handling, cleaning services, and security inspections, ensuring smoother and more efficient passenger experiences.
Are there autonomous robots being developed for aviation applications?
Yes, autonomous robots are being developed for tasks such as runway inspection, aircraft refueling, and de-icing operations, aiming to enhance operational efficiency and safety in airports and on the airfield.
What are the future prospects of robotics in air traffic control?
Robotics could potentially assist in air traffic management by analyzing real-time data, optimizing flight routes, and improving communication between air traffic controllers and pilots, leading to enhanced safety and airspace utilization.
Video Explanation
The video below will provide more information as to how this technology works
Example Industry User

Boston Dynamics is a leading innovator in robotics, renowned for developing highly advanced and versatile robots that mimic human and animal movements. Their robots, such as the humanoid Atlas and the quadruped Spot, showcase cutting-edge capabilities in mobility, agility, and autonomy. By pushing the boundaries of robotic engineering, Boston Dynamics aims to create machines that can perform complex tasks in diverse environments, ranging from industrial applications to disaster response. This relationship highlights Boston Dynamics’ pivotal role in advancing the field of robotics and transforming how robots can be integrated into various sectors.
Further Resources
Below are some external links to further information on this technology.