Internet of Things (IoT)
What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity. These smart devices can collect and share data, enabling them to communicate with each other and with other internet-enabled devices. Here are some key points about IoT:
Smart Objects
IoT devices, also known as “smart objects,” can range from simple smart home devices like thermostats to wearables like smartwatches and even complex industrial machinery.
Interconnected Devices
IoT enables these devices to exchange data autonomously. For example:
- Monitoring environmental conditions on farms.
- Managing traffic patterns with smart cars and other automotive devices.
- Controlling machines and processes in factories.
- Tracking inventory and shipments in warehouses.
Impact Across Industries
IoT has applications in various industries, including manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, and agriculture. As the number of internet-connected devices continues to grow, IoT is likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping our world.
Business Benefits
- Improved Efficiency: By automating and optimizing processes, businesses can enhance efficiency and productivity. For instance, IoT sensors can monitor equipment performance, detect potential issues, and reduce maintenance costs.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: IoT generates vast amounts of data that businesses can analyze to gain insights into customer behaviour, market trends, and operational performance. This informs better-informed decisions about strategy, product development, and resource allocation.
- Cost-Savings: Automation through IoT helps reduce manual processes, cut costs, and improve profitability. For example, monitoring energy usage optimizes consumption, leading to energy cost savings and improved sustainability.
In summary, IoT is transforming the way we live, work, and interact with each other, creating a connected ecosystem of smart devices that enhance our daily lives and business operations.
IoT in the Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing operations both on the ground and in the air. For example:
Manufacturing Efficiency
- IoT enables advanced analytics that provide insights post-flight. Manufacturers can rapidly address inefficiencies based on real-time data.
- Smart meters with IoT capabilities offer information on energy usage during aircraft production. This can lead to significant cost savings and more sustainable operations. By analysing usage patterns and suggesting energy-saving measures, energy consumption can be reduced by up to 20%.
- Real-time monitoring of shop floors allows for accurate simulations and optimization of operations. For instance, Airbus’ Saint Eloi factory creates a “digital shadow” of the entire assembly line using data from machines and conveyors.
Quality and Productivity Improvements
- IoT helps monitor and control critical parameters during assembly. For example, it can track the torque provided by tools on the assembly line, ensuring consistent quality.
- Real-time analytics allow for better decision-making, leading to improved productivity and quality rates.
Enhanced Passenger Experiences
- IoT extends beyond manufacturing. Passengers can look forward to exciting new in-flight experiences. Connected cabin systems can personalize services, adjust lighting, and optimize comfort based on individual preferences.
- Real-time data from IoT sensors can enhance safety measures and overall passenger satisfaction.
In summary, IoT in the aerospace industry is driving efficiency, quality, and innovation, benefiting manufacturers, passengers, and the entire aviation ecosystem.
Evolution of The Internet of Things (IoT)
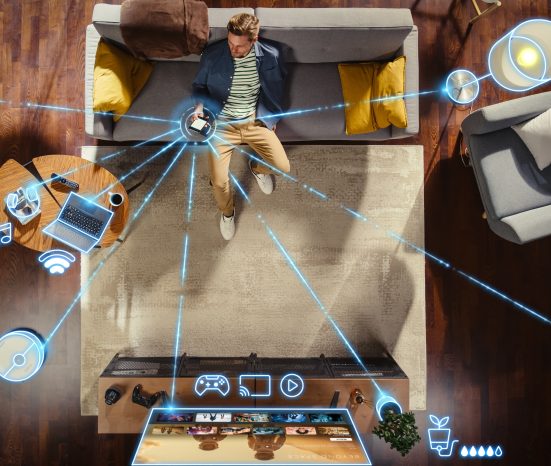

The evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed everyday objects into interconnected devices capable of exchanging data over the internet. Originating from the concept of machine-to-machine communication, IoT has expanded to include a vast array of applications across industries. Early IoT devices focused on monitoring and automation, but advancements in sensor technology, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence have enabled more sophisticated applications in smart homes, healthcare, transportation, and industrial sectors. As IoT continues to grow, it promises to revolutionize how businesses operate and how people interact with technology in the digital age.
Aerospace & IoT in Future
In the future of aerospace, IoT is poised to revolutionize operations, safety, and passenger experience. IoT-enabled sensors and devices will enhance real-time monitoring of aircraft systems, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Smart airports equipped with IoT technology will optimize ground operations, from baggage handling to security protocols, improving efficiency and passenger flow. Moreover, IoT applications in aerospace will contribute to enhanced communication and navigation systems, supporting safer and more reliable air travel globally.

Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions and answers pertaining to the IoT, especially in regards to aviation.
How is IoT used in aviation maintenance?
IoT in aviation maintenance involves sensors and connected devices monitoring aircraft systems in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing unplanned downtime.
What are some examples of IoT applications in aircraft operations?
IoT applications in aircraft operations include real-time monitoring of fuel consumption, engine performance, and cabin conditions, optimizing efficiency and passenger comfort.
Can IoT improve air traffic management?
Yes, IoT can enhance air traffic management by providing real-time data on aircraft positions, weather conditions, and airport operations, optimizing flight routes and airspace utilization.
What are the security implications of IoT in aviation?
Security concerns include safeguarding IoT devices from cyber threats, ensuring data integrity, and maintaining secure communication channels to prevent unauthorized access to critical aviation systems.
How might IoT enhance the passenger experience in aviation?
IoT can improve the passenger experience by offering personalized services, such as automated check-in processes, real-time flight updates, and in-flight entertainment options tailored to passenger preferences.
Video Explanation
The video below will provide more information as to how this technology works
Example Industry User

Chelton, a leader in advanced communication systems, is harnessing the Internet of Things (IoT) to enhance its product offerings and operational capabilities. By integrating IoT technology, Chelton enables seamless connectivity and real-time data exchange between its communication devices and systems. This allows for improved monitoring, maintenance, and performance optimization, particularly in demanding environments like aerospace and defense. IoT integration supports Chelton’s commitment to providing cutting-edge, reliable communication solutions that meet the evolving needs of its customers.
Further Resources
Below are some external links to further information on this technology.